You want to schedule a list of jobs in d days. Jobs are dependent (i.e To work on the ith job, you have to finish all the jobs j where 0 <= j < i).
You have to finish at least one task every day. The difficulty of a job schedule is the sum of difficulties of each day of the d days. The difficulty of a day is the maximum difficulty of a job done on that day.
You are given an integer array jobDifficulty and an integer d. The difficulty of the ith job is jobDifficulty[i].
Return the minimum difficulty of a job schedule. If you cannot find a schedule for the jobs return -1.
Example 1:
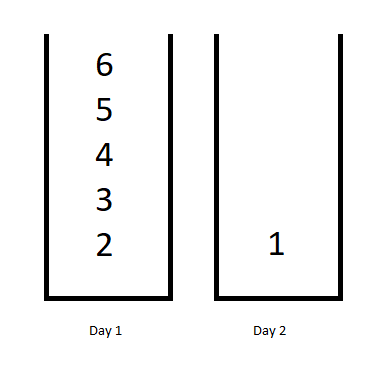
Input: jobDifficulty = [6,5,4,3,2,1], d = 2 Output: 7 Explanation: First day you can finish the first 5 jobs, total difficulty = 6. Second day you can finish the last job, total difficulty = 1. The difficulty of the schedule = 6 + 1 = 7
Example 2:
Input: jobDifficulty = [9,9,9], d = 4 Output: -1 Explanation: If you finish a job per day you will still have a free day. you cannot find a schedule for the given jobs.
Example 3:
Input: jobDifficulty = [1,1,1], d = 3 Output: 3 Explanation: The schedule is one job per day. total difficulty will be 3.
Constraints:
1 <= jobDifficulty.length <= 3000 <= jobDifficulty[i] <= 10001 <= d <= 10
To solve this problem efficiently using dynamic programming (DP), we need to approach it by dividing the list of jobs into d non-empty subarrays. The problem is about finding the minimum difficulty schedule, where the difficulty of each subarray is the maximum difficulty of the jobs scheduled on that day.
Problem Breakdown:
- We are tasked with dividing the jobs into
dgroups (or days). Each group must contain at least one job. - The difficulty of a day is the maximum difficulty of any job assigned to that day, and the total difficulty of the schedule is the sum of the maximum difficulties across all days.
Approach:
Dynamic Programming Approach:
We'll use a 2D DP array dp[i][j] where:
irepresents the number of jobs considered.jrepresents the number of days used to schedule the firstijobs.dp[i][j]will store the minimum difficulty for scheduling the firstijobs intojdays.
Steps:
-
Base Case:
dp[0][0] = 0: No jobs, no days, zero difficulty.dp[i][0] = infinityfori > 0: Impossible to schedule jobs with zero days.dp[i][j] = infinityinitially for all other values, indicating impossible cases.
-
DP Transition:
- For each possible number of days
j, and for each possible last jobiin the partition, we calculate the difficulty of the current day. This is done by considering all jobs from some earlier jobktoias part of the last day and computing the maximum difficulty for that day. - For each partition from
ktoi, updatedp[i][j]as: - This way, we try to partition the jobs into
jgroups, calculating the difficulty of each partition.
- For each possible number of days
-
Final Answer:
- After filling the DP table, the result will be in
dp[n][d]wherenis the total number of jobs anddis the number of days.
- After filling the DP table, the result will be in
-
Edge Case:
- If the number of jobs is less than the number of days (
n < d), return-1because it's impossible to schedule jobs.
- If the number of jobs is less than the number of days (
Code Implementation:
public class Solution {
public int MinDifficulty(int[] jobDifficulty, int d) {
int n = jobDifficulty.Length;
// Edge case: If there are fewer jobs than days, return -1
if (n < d) return -1;
// DP array where dp[i][j] represents the minimum difficulty of scheduling first i jobs into j days
int[,] dp = new int[n + 1, d + 1];
// Initialize the dp array with a large number (int.MaxValue)
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= d; j++) {
dp[i, j] = int.MaxValue;
}
}
// Base case: 0 jobs and 0 days results in 0 difficulty
dp[0, 0] = 0;
// Iterate over number of days
for (int j = 1; j <= d; j++) {
// Iterate over number of jobs to be scheduled
for (int i = j; i <= n; i++) { // Need at least 'j' jobs to schedule 'j' days
int maxJobDifficulty = 0;
// Try partitioning the jobs in different ways
for (int k = i - 1; k >= j - 1; k--) {
maxJobDifficulty = Math.Max(maxJobDifficulty, jobDifficulty[k]);
dp[i, j] = Math.Min(dp[i, j], dp[k, j - 1] + maxJobDifficulty);
}
}
}
// The answer is the minimum difficulty of scheduling all jobs in 'd' days
return dp[n, d];
}
}
Explanation:
-
DP Table Initialization:
- We initialize a DP table
dp[n+1][d+1]with a very large value (int.MaxValue) to indicate that a schedule is not possible for that configuration. We also set the base casedp[0][0] = 0, as there is no difficulty when there are no jobs and no days.
- We initialize a DP table
-
DP Transitions:
- We iterate over each possible day count (
j), and for each day, we check how to split the firstijobs intojgroups. We consider each possible partition fromktoi, wherekis the job index before the current partition. - For each partition, we compute the maximum job difficulty for the jobs assigned to that day and add it to the previous day's difficulty (
dp[k][j-1]).
- We iterate over each possible day count (
-
Final Answer:
- Once all the DP table entries are filled,
dp[n][d]holds the minimum possible difficulty for scheduling allnjobs intoddays.
- Once all the DP table entries are filled,
Time Complexity:
- Time Complexity:
O(n * n * d). We have three nested loops:- The outer loop runs
dtimes (for the days). - The second loop runs
ntimes (for the jobs). - The innermost loop runs up to
ntimes (to check all possible previous jobs in the current partition).
- The outer loop runs
- Space Complexity:
O(n * d)for the DP table.
Example Walkthrough:
Example 1:
Input:
jobDifficulty = [6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1], d = 2
Output:
7
- Day 1: Jobs
[6, 5, 4, 3, 2](max difficulty = 6). - Day 2: Jobs
[1](max difficulty = 1). - Total difficulty = 6 + 1 = 7.
Example 2:
Input:
jobDifficulty = [9, 9, 9], d = 4
Output:
-1
- More days than jobs, so it's impossible to schedule.
Example 3:
Input:
jobDifficulty = [1, 1, 1], d = 3
Output:
3
- Each day gets one job, and the difficulty of each day is 1.
- Total difficulty = 1 + 1 + 1 = 3.
This dynamic programming approach ensures that we explore all valid job partitions while optimizing for the minimum difficulty. Let me know if you have more questions!
